Tutorial courtesy of Dean Frate
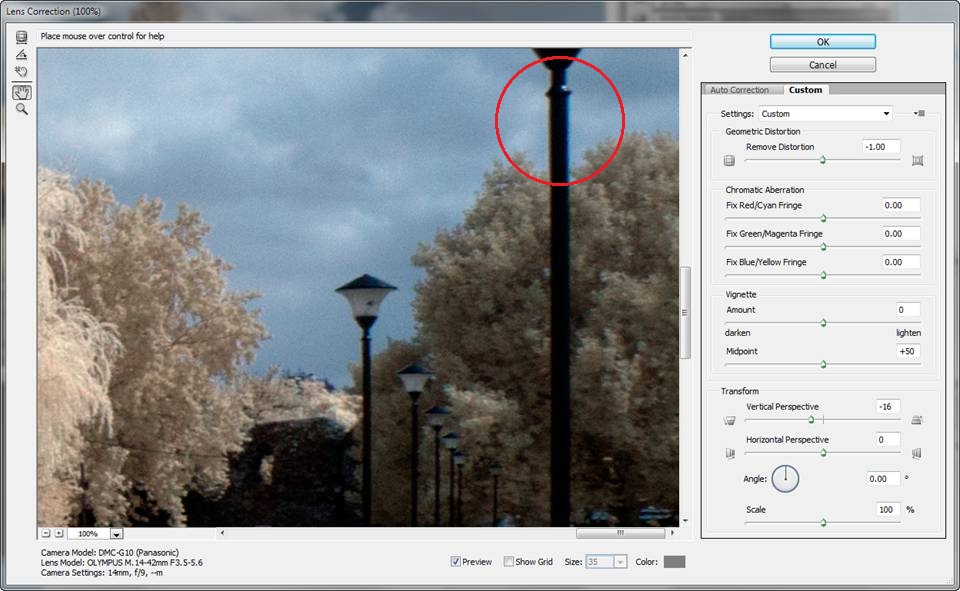
The angle that the camera is held at, the barrel or pincushion characteristics of the lens, and the chromatic separation inherent to the lens and the wavelengths allowed to hit the sensor all contribute to image distortion. With infrared these issues can be more pronounced, since most lenses aren’t designed for the infrared spectrum. Playing with the various setting will give a good idea of what they do. It’s instructive to push the sliders to the max in either direction to understand the effect, before settling on a final setting. Note the chromatic aberration particularly around the light post in the foreground and that the corrective settings seem to echo Lab color space opposites.
First load the Lens Correction filter.
 |
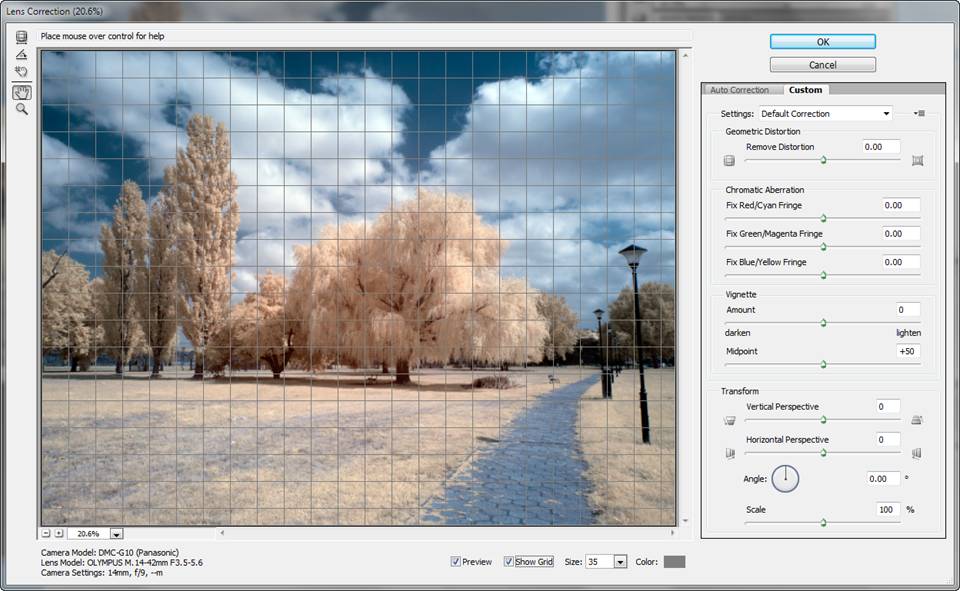
Use the Transform and Geometric Distortion sliders to correct perspective and pincushion/barrel in the image.
 |
This is the result of the settings below.
 |
Zoom in and look for light/dark transition areas to evaluate and correct chromatic aberration.
 |
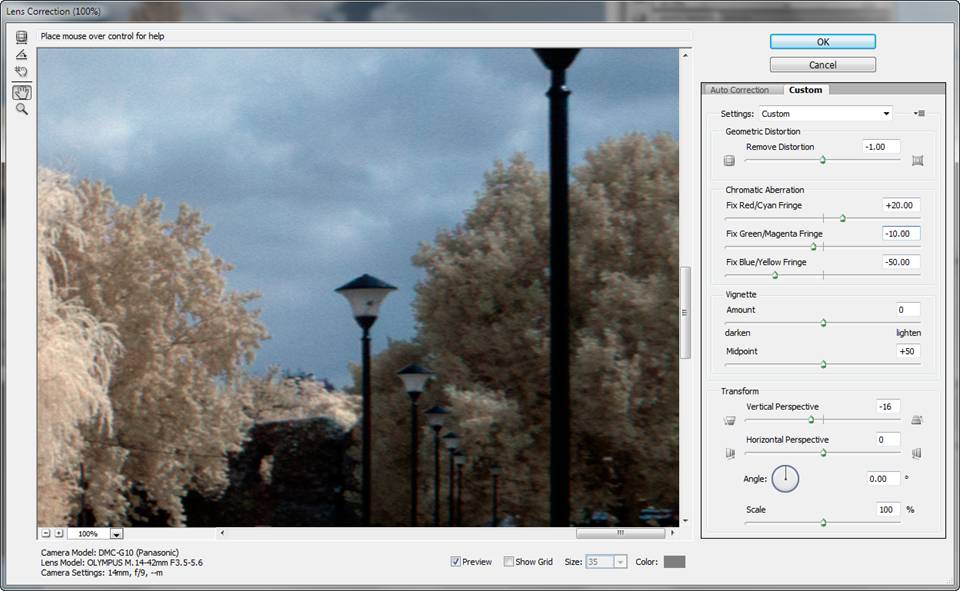
This is what the correction yields.
 |





Lightroom has an unsupported (but distributed on the Adobe site) plug-in for “flat field correction.” It can be found here:
http://labs.adobe.com/downloads/lightroomplugins.html
Can this process and plug-in be used to correct lenses, especially native Sony lenses, used with the thin sensor glass modification?
Thanks,
Bob
Thank you for your help. I’ve just begun the ir learning curve. I have a Sony NEX5 converted to 470nm. I am considering using an additional filter to achieve additional effects. I use PS cc and have loaded the Nik collection and Moody actions. I shoot raw and use Capture One Pro. So far I’m having a lot of fun but don’t yet know what my perimeters are. I’ll keep studying.